

So we're going to go ahead and take a look at the units for the gas constant, which is leaders, times, atmospheres over moles, times kelvin's. So we are given the pressure in seven 80 millimeters of mercury and were asked what gas unit to convert that millimeters of mercury into if we want to use it in the ideal gas law. So we do this calculation, we get a final pressure of 1.56 atmospheres, and that is our final answer for part B.Alright in this question, were given a pressure in one gas unit and were asked to determine whether what kind, what gas unit we need if we want to use the ideal gas law. We got one points your 6263 80 m multiply pie 301 Calvin that is equal to P two, multiplied by 1 98 Kelvin provide both sides by 1 98 and this calculation gives us a final pressure. Over the initial temperature, which is 1 90 80 Calvin that is equal to the final pressure, which we're solving for divided by the final temperature, which is 301 Kelvin. So that is our and initial pressure an ATM, and now we can go ahead and use RP one over t one equals P two over t two. So after we do visibly this calculation, we get an initial pressure of one point 0 to 63 atmospheres. So if we take this, um, 780 millimeters of mercury, that will be equal to one atmosphere divided by 7 16 millimeters of mercury. Hum because 760 millimeters of mercury is equal to one atmosphere. Pressure is given to us in millimeters of mercury, and we can convert this into atmospheres. Now the question asks us to find the final pressure atmospheres and her party are.
780 mmhg to atm plus#
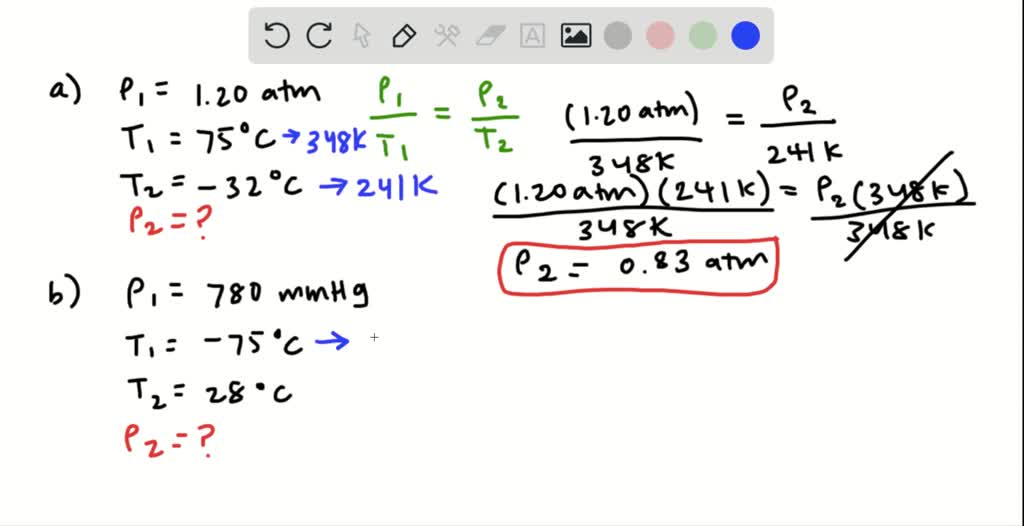
We have negative 75 degrees Celsius plus 2 73 I was ableto 1 98 kelvin in our 28 degrees plus 2 73 is equal to 301 Calvin. So we gonna converted temperatures in the Taliban again. Uh, we're gonna use the same equation and have to do some conversions first. That is the answer for the final pressure for part A. So we got one point 2018 multiplied by 2 41 OK, that is equal to P two won't apply by 3 48 k can divide both sides by 3 48 Who canceled this out so that we can isolate for P two 1.2 multiplied by 2 41 founded by 3 48 in that is equal to about 0.83 a. And that is equal to our final pressure, which you're solving for divided by our final temperature, which is 241 Calvin and we can cross multiply. It's 1.20 atmospheres divided by initial temperature, which is 348 Calvin. So if we said what we have to the equation, you have initial pressure. We do the same thing for final temperature, and I get a 32 degrees Celsius plus 2 73 and our final temperature is 2 41 killed in. So for initial temperature, at 75 we had to 73. So to do this, we just take our degrees in Celsius. But first, we have to convert our temperature into Kelvin because that is the units that we need not to use this equation. So we can seven what we have to the equation. And this is because pressure is proportional to temperature. Ziegel to final pressure divided about divided by final temperature. Now, to find file pressure, we can use the equation, which is gay loose tax law, which is initial pressure divided by initial temperature. So starting with part A, we have an initial pressure of 1.20 atmospheres, initial temperature and a final temperature of 75 degrees Celsius and negative 32 degrees Celsius.

We have to calculate the final pressure in atmospheres, uh, with a constant moles and volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
